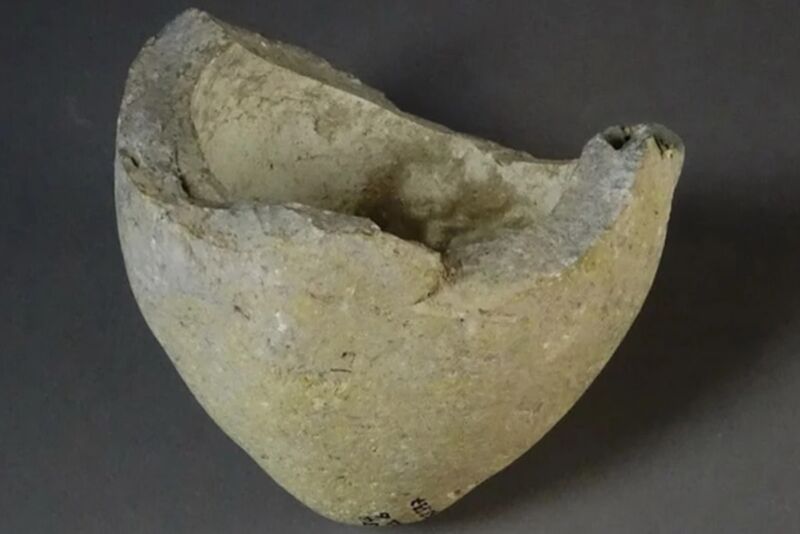
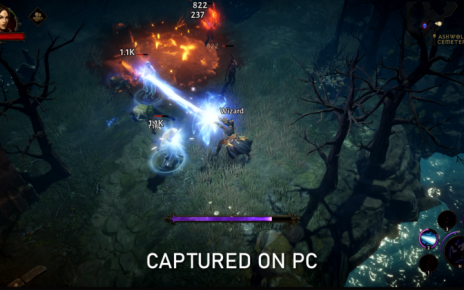
Enlarge / Analysis of the residue inside this shard from the ceramic vessel indicates it may have been used as a new hand grenade. The shard was excavated from a site in Jerusalem in the 1960s, and dates back to the 11th or 12th century CE. (credit: C. D. Matheson et al., 2022)
Archaeologists have analyzed the remains inside four medieval ceramic shards and determined that one of them may have been used as a hand grenade, according to a recent paper published within the journal PLOS One. And the explosive used was likely made locally rather than gunpowder imported from China.
Byzantine soldiers used early versions of grenades in the 8th century CE, building on the ” Greek fire ” invented some sort of century earlier. Instead of using Greek fire with flamethrowers, they placed the incendiary material inside small stone or ceramic (and later, glass) jars to create handheld explosives. By the 10th century, the technology had spread to China, with Chinese troops packing gunpowder into ceramic or metal containers with a fuse attached.
India likely also had grenade-like weapons. A 12th century manuscript (based on an earlier Sanskrit work) describes a terra-cotta elephant filled with explosives with a fuse that was unleashed on an invading army. A mid-14th century Chinese treatise references a “flying-cloud thunderclap cannon, ” described as cast iron shells shaped like a good ball and roughly the size of a bowl, filled along with gunpowder (“divine fire”). Similar grenades first appeared in Europe in 1467 and have been a staple of warfare since.