Enlarge (credit: Jason Persoff / Getty Images)
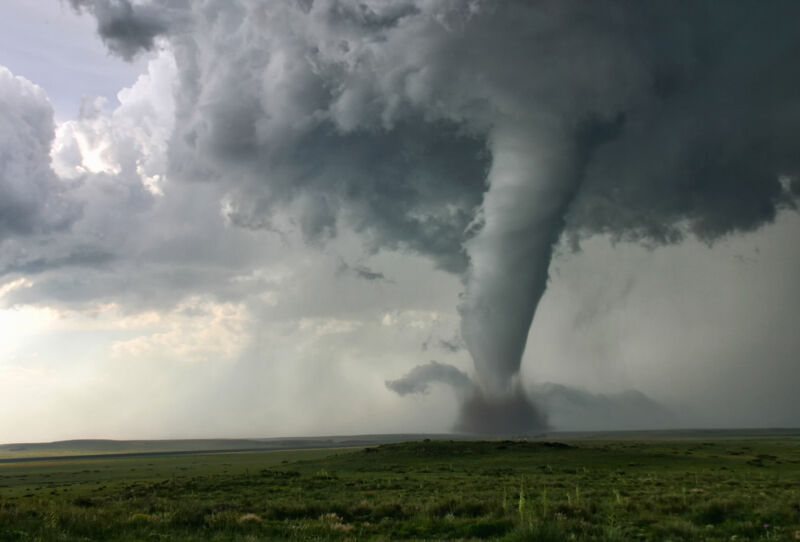
Recently, a network of climate modeling groups showed that it will cost more to overshoot the Paris Agreement temperature goals than it will to stay on a low-temperature trajectory. On the same day, that collaboration also published work showing that additional risks of overshooting come in part via ensuing increases in extreme weather.These studies are two of four published this year; together they provide the most comprehensive projections of the requirements and implications of the path we take to reach our end-of-century temperature targets.
The article focused on the economic aspects of meeting the Paris temperature targets—specifically how much mitigation actions will cost and the impact on the global GDP—wasn’t designed to project environmental impacts. In fact, most economic models don’t include this level of complexity and, as a result, they underestimate the overall costs. But this additional analysis projects not only how much extreme weather will increase, but also how that will effect crop yields around the world.
“The decarbonization scenarios reviewed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in the last assessment reports do not account for the climate impacts’ feedback. The main reason is that [there are] many uncertainties surround the geophysical and economic impacts of climate change, making their integration difficult in the design of decarbonization pathways,” wrote first author Dr. Laurent Drouet in an email to Ars Technical. Drouet is a researcher at the RFF-CMCC European Institute of Economics and the Environment, in Milan, Italy. “But, now, [our] research focuses on improving the representation of these impacts and producing results that are easier to integrate into mitigation models.”