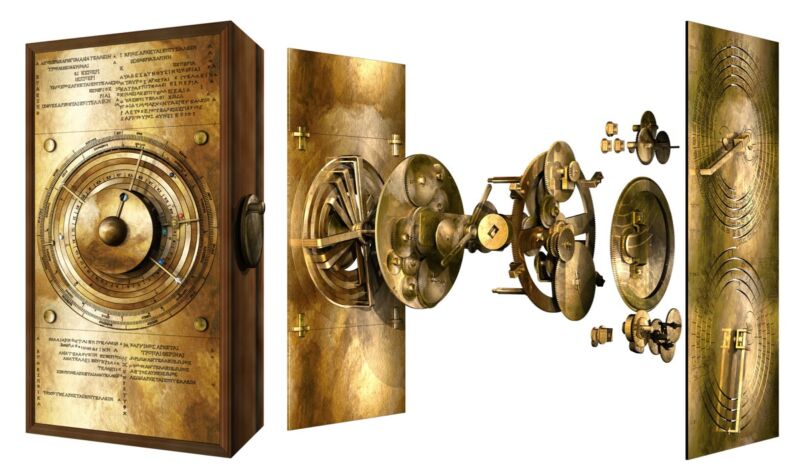
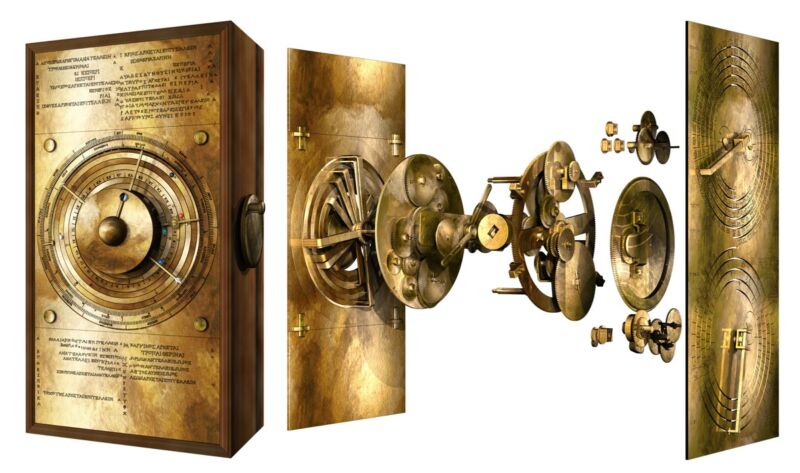
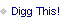Enlarge / “Exploded” view of the new computer model of the Antikythera mechanism, showing how it might have worked. (credit: Tony Freeth)
Scientists have long struggled to solve the puzzle of the gearing system on the front of the so-called Antikythera mechanism—a fragmentary ancient Greek astronomical calculator, perhaps the earliest example of a geared device. Now, an interdisciplinary team at University College London (UCL) has come up with a computational model that reveals a dazzling display of the ancient Greek cosmos, according to a new paper published in the journal Scientific Reports. The team is currently building a replica mechanism, moving gears and all, using modern machinery. You can watch an extensive 11-minute video about the project here (embedding currently disabled).
“Ours is the first model that conforms to all the physical evidence and matches the descriptions in the scientific inscriptions engraved on the mechanism itself,” said lead author Tony Freeth, a mechanical engineer at UCL. “The Sun, Moon, and planets are displayed in an impressive tour de force of ancient Greek brilliance.”
“We believe that our reconstruction fits all the evidence that scientists have gleaned from the extant remains to date,” co-author Adam Wojcik, a materials scientist at UCL, told the Guardian.