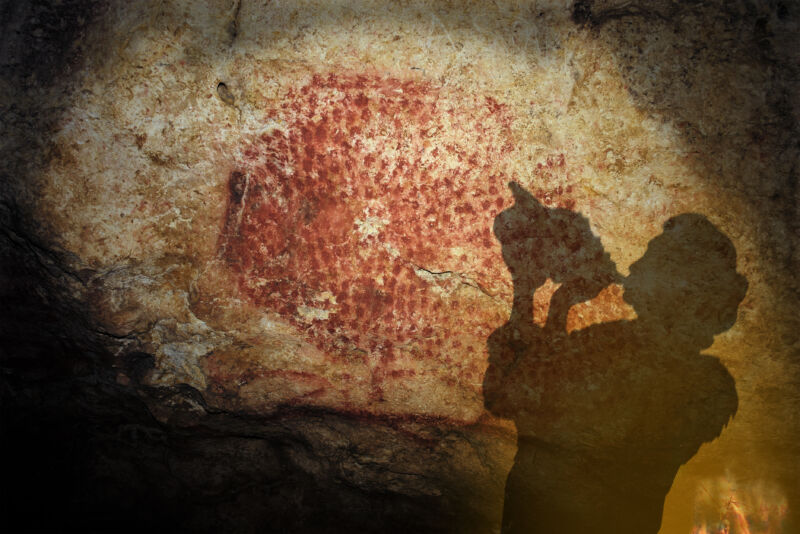
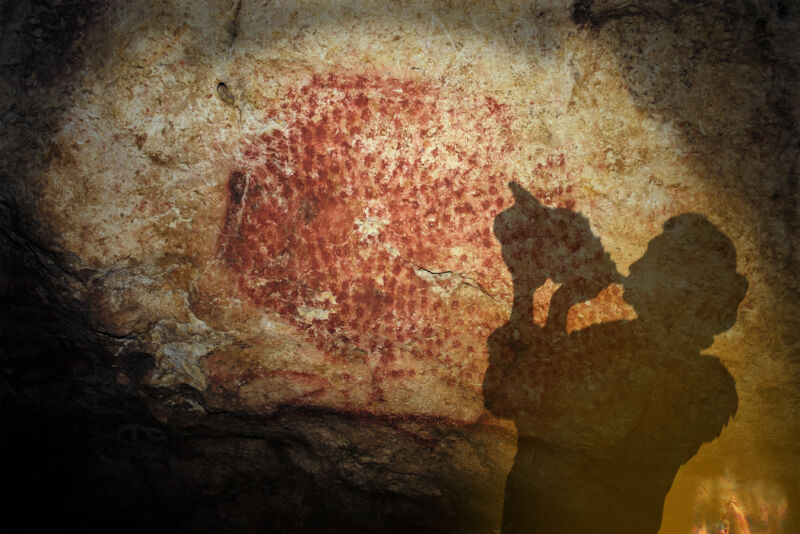
Enlarge / Archaeologists in 1931 found the conch shell near the entrance of Marsoulas Cave. This is a reconstruction of where and how the shell might have been played. (credit: G. Tosello)
After 18,000 years of silence, an ancient musical instrument played its first notes. The last time anyone heard a sound from the conch shell trumpet, thick sheets of ice still covered most of Europe.
University of Toulouse archaeologist Carole Fritz and her colleagues recently recognized the shell as a musical instrument. To understand more about how ancient people crafted a trumpet from a 31cm (1 foot) long conch shell, the archaeologists used high-resolution CT scans to examine the shell’s inner structure: delicate-looking whorls of shell and open chambers, coiled around a central axis, or columella. A series of overlapping photographs and careful measurements became a full-color, 3D digital model of the shell, and image enhancement software helped reveal how Magdalenian people had decorated the instrument with red ocher dots.
And in a lab at the University of Toulouse, a horn player and musicology researcher became the first person in 18,000 years to play the conch shell. The musician blew into the broken tip, or apex, of the shell and vibrated his lips as if he were playing a trumpet or trombone. Very carefully, he coaxed three loud, clear, resonant notes from the ancient instrument: